17) Umpolung Of 4,4-Disubstituted 2-Hydroxycyclohexa-2,5-Dienones for The Regiodivergent Synthesis ff Disubstituted Catechols
Ryunosuke Akazawa, Ahmed A.B. Mohamed, Kenzo Yahata, Kohei Miyagaki, Masaki Togami, Yoshinari Sawama, Kyohei Kanomata, Shuji Akai*
Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2024, 97, uoae111.
DOI: 10.1093/bulcsj/uoae111.
Selected as a BCSJ Award Article
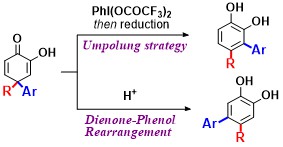

Abstract: The umpolung of 4,4-disubstituted 2-hydroxycyclohexa-2,5-dienones 1 with PhI(OCOCF3)2 achieved the migration into the more electron-rich C3position, providing exclusively 3,4-disubstituted catechols 3. Acid-induced rearrangement of 1 produced 4,5-disubstituted catechols 2. These two reactions enabled the highly selective production of two regioisomers of disubstituted catechols, especially biaryls containing catechol moieties,
from the common intermediates 1.

16) Photocatalytic Multiple Deuteration of Polyethylene Glycol Derivatives using Deuterium Oxide
Riku Ogasahara, Miyu Mae, Keisuke Matsuura, Sota Yoshimura, Takayoshi Ishimoto, Taro Udagawa, Kazuo Harada, Hiroyoshi Fujioka, Mako Kamiya, Rio Asada, Hiromasa Uchiyama, Yuichi Tozuka, Shuji Akai, Yoshinari Sawama*
ChemRxiv (2024)
DOI:10.26434/chemrxiv-2024-s6gmv
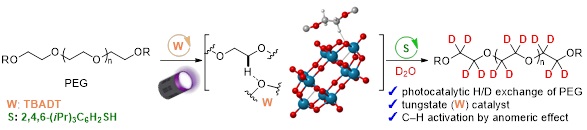
Abstract: Deuterated molecules are of growing interest because of the specific characteristics of deuterium, such as stronger C-D bonds being stronger than C-H bonds. Polyethylene glycols (PEGs) are widely utilized in scientific fields (e.g., drug discovery and material sciences) as linkers and for the improvement of various properties (solubility in water, stability, etc.) of mother compounds. Therefore, deuterated PEGs can be used as novel tools for drug discovery. Although the H/D exchange reaction (deuteration) is a powerful and straightforward method to produce deuterated compounds, the deuteration of PEGs bearing many unactivated C(sp3)-H bonds has not been developed. Herein, we report the photocatalytic deuteration of multiple PEGs using tetra-n-butylammonium decatungstate (TBADT) and D2O as an inexpensive deuterium source. This deuteration can be adapted to PEG derivatives bearing various substituents ((hetero)aryl, benzoyl, alkyl, etc.). The deuteration efficiencies of the α-oxy C(sp3)-H bonds at the terminal positions of the PEGs were strongly influenced by the substituents. These reactivities were elucidated by density functional theory calculations of the reaction barriers towards the formation of radical intermediates, induced by the excited state of TBADT and the PEG substrate. In addition, the applicability of deuterated PEGs to internal standard experiments and Raman spectroscopy was demonstrated.

15) Photocatalytic and Highly Regioselective H/D Exchange at α-thio C(sp3)-H Bonds
Riku Ogasahara, Miyu Mae, Yuki Itabashi, Kei Ohkubo, Keisuke Matsuura, Hyoga Shimizu, Kazuho Ban, Taro Udagawa, Hiroyoshi Fujioka, Mako Kamiya, Shuji Akai, Yoshinari Sawama*
(RO and MM equally contributed.)
ChemRxiv (2024)
DOI:10.26434/chemrxiv-2024-pc5qz
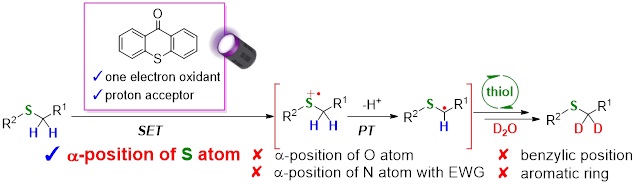
Abstract: Deuterated compounds used in drug discovery and live-cell imaging have recently gained the attention of various scientific fields. Although hydrogen-deuterium (H/D) exchange reactions are straightforward deuteration methods, achieving perfect regioselectivity is challenging. We report the highly regioselective deuteration of α-thio C(sp3)-H bonds using a thioxanthone or anthraquinone organic photocatalyst bearing an aromatic ketone skeleton and D2O as an inexpensive deuterium source under 390-nm irradiation. Notably, deuterium incorporation at the α-positions of O/N atoms, benzylic positions, and aromatic rings was not observed. The present regioselectivity was accomplished via a single electron transfer mechanism between the photocatalyst and S-containing substrates, as proven by laser-induced time-resolved transient absorption spectroscopic measurements. Furthermore, the proposed deuteration method could be applied to various S-containing substrates including pharmaceuticals and biologically active compounds with high regioselectivities. The available deuterated compounds as novel deuterated alkylation reagents for future drug discovery and as materials for Raman imaging were also demonstrated.

14) Deuterated-Alkylation Reagents based on Sulfonium Salts as Cation and Radical Sources
Kazuho Ban, Jin Tokunaga, Sota Yoshimura, Shuji Akai, Yoshinari Sawama*
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, accepted 2024, 97, uoae109.
DOI: doi.org/10.1093/bulcsj/uoae109
Selected Article
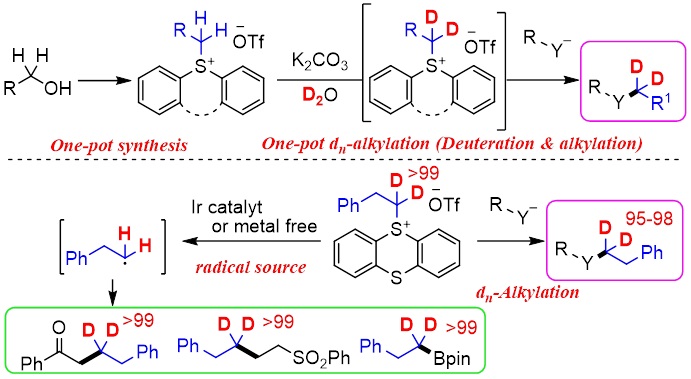

Abstract: The replacement of C-H bonds with more stable C-D bonds at the α-position of heteroatoms, which is the typical metabolic site for cytochrome P450, is important in drug discovery. Recently, we have developed dn (deuterated)-alkylated sulfonium salts (1a–dn), which were easily prepared by deuteration (H/D exchange reaction) with D2O of the corresponding alkyl diphenylsulfonium salts (1a), as electrophilic dn-alkylating reagents (cation sources). Herein, we newly report an improved preparation method of 1a and one-pot synthesis of dn-alkylated compounds via the deuteration of 1a with D2O and the subsequent nucleophilic substitution under basic conditions. Additionally, dn-alkyl thianthrenium salts (1b–dn) were also found to work as dn-alkylating reagents (cation sources). Furthermore, 1b–dn served as radical sources under photo-induced reaction conditions with Ir photocatalyst, Hantzsch ester, or triphenylamine to obtain various regioselectively deuterium-incorporated alkyl compounds. These dn-alkylating reagents will contribute to advance the drug discovery.

13) Raman optical activity study of deuterated sugars: deuterium labelling as a tool to analyze stereochemistry and conformation
Tohru Taniguchi, Davidson Obinna Agbo, Qin Yang, Josef Kapitán, Tao Wu, Shuki Oyama, Shuji Akai, Yoshinari Sawama, and Petr Bouř
Phy. Chem. Chem. Phys. (2024), 2024, 26, 21568–21574.
DOI: doi.org/10.1039/D4CP02406K
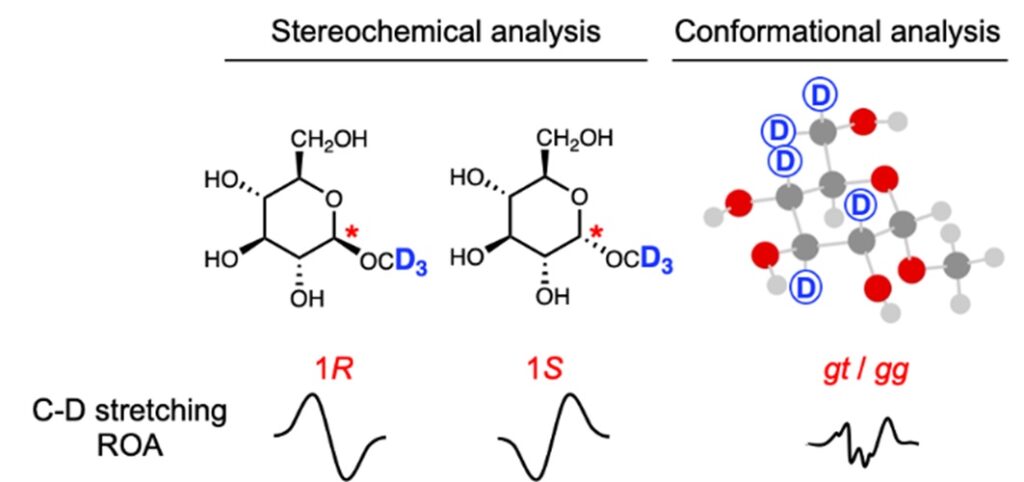
Abstract: Structural analyses using Raman optical activity (ROA) spectroscopy conventionally rely on vibrational signals in the fingerprint region ranging from 100 to 1800 cm-1. Use of deuterium labelling to observe ROA signals in the C-D stretching region provides additional information about a local structure of large molecular systems. So far, the potential of C-D stretching ROA signals for structural analysis has rarely been explored. In the present work, we synthesized model deuterated glucose monosaccharides and studied their ROA properties by employing molecular dynamics and density functional theory to interpret the spectra. A good agreement between the simulated and experimental spectra is achived when the proper conformer ratios are considered. This shows the usefulness of ROA spectroscopy assisted by deurium labelling for stereochemical and conformational analysis.
12) Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of 2-Hydroxybiaryl Atropisomers via Lipase-Catalyzed Enantioselective O-Acylation
Neha Dhiman, Gamal A. I. Moustafa, Kengo Kasama, Hiroshi Aoyama, Kyohei Kanomata, Harald Gröger,* Shuji Akai*
ChemCatChem 2024, e202400932.
DOI: doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202400932

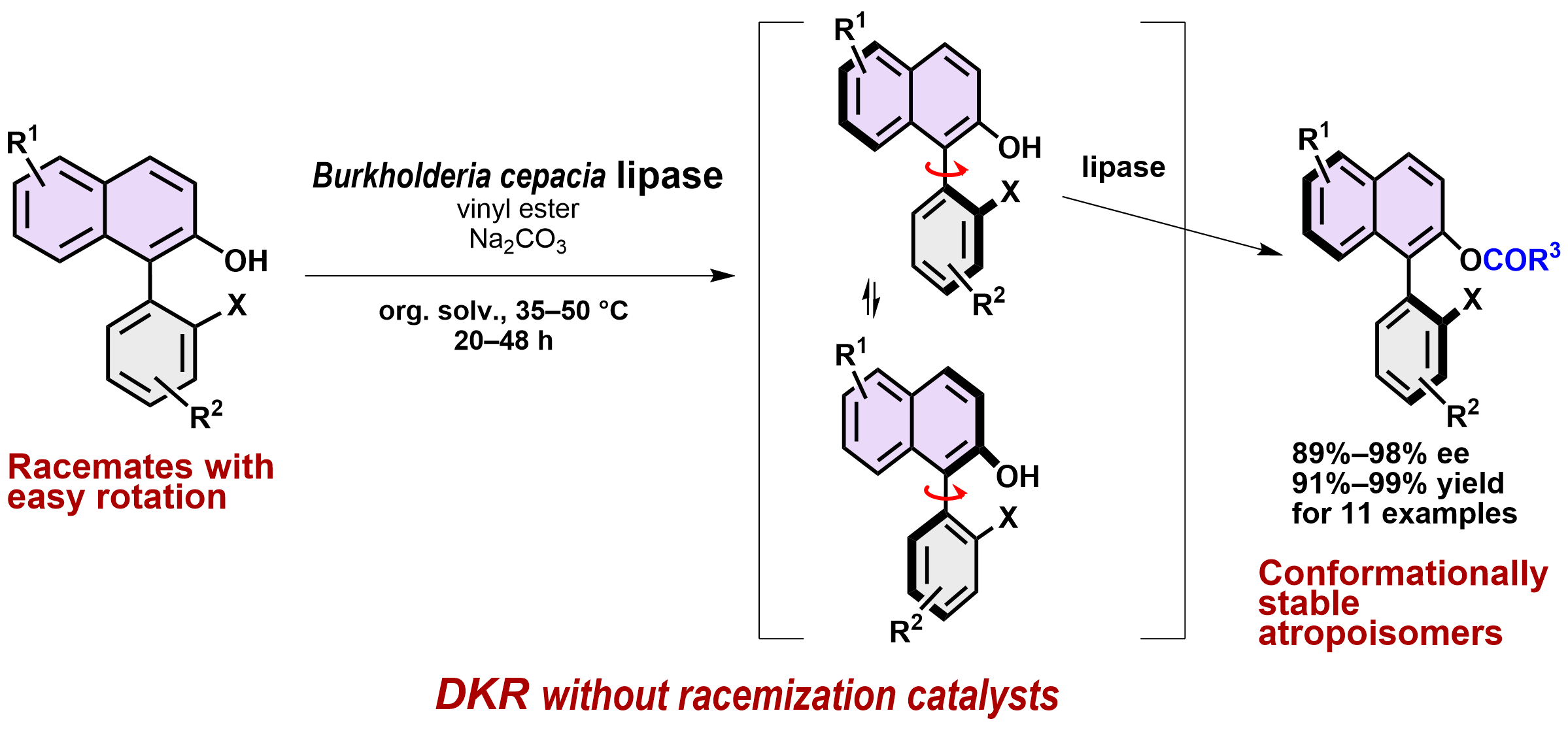
Abstract: The increasing interest in axially chiral biaryl moieties, which are prevalent in chiral ligands, organocatalysts, and bioactive molecules, has raised the need for developing novel efficient synthetic methods for these types of molecules. In addition to the currently available methods, such as kinetic resolution, desymmetrization and enantio- and diastereo-selective biaryl coupling, we herein report a lipase-catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) of racemic 2-hydroxybiaryls through enantioselective O-acylation. This method features the production of enantiomerically enriched atropisomers (89%–98% ee) in 91%–99% yields from eleven racemates. Notably, the DKR proceeds without any racemization catalyst since in situ-racemization was achieved by easy rotation about the biaryl axis of the substrates. The enzymatic O-acylation then furnished conformationally stable biaryl-containing esters, in which the increased steric bulkiness of the O-acyl moiety suppresses the rotation, i.e., racemization, under the reaction conditions of 35–50 °C. This experimental study was accompanied by a computational determination of the rotational barrier of substrates and products. The choice of suitable substrates with a significant difference in their rotational barrier compared to that of their products turned out to be the key to an efficient implementation of this method.

11) Deuterated Alkyl Sulfonium Salt Reagents; Importance of H/D Exchange Methods in Drug Discovery
Riku Ogasahara, Kazuho Ban, Miyu Mae, Shuji Akai, Yoshinari Sawama*
ChemMedChem (Concept), 2024, e202400201 (Open Access).
DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202400201
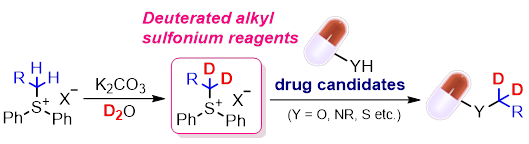
Abstract: Deuterated drugs (heavy drugs) have recently been spotlighted as a new modality for small-molecule drugs because the pharmacokinetics of pharmaceutical drugs can be enhanced by replacing C-H bonds with more stable C-D bonds at metabolic positions. Therefore, deuteration methods for drug candidates are a hot topic in medicinal chemistry. Among them, the H/D exchange reaction (direct transformation of C-H bonds to C-D bonds) is a useful and straightforward method for creating novel deuterated target molecules, and over 20 reviews on the synthetic methods related to H/D exchange reactions have been published in recent years. Although various deuterated drug candidates undergo clinical trials, approved deuterated drugs possess CD3 groups in the same molecule. However, less diversification, except for the CD3 group, is a problem for future medicinal chemistry. Recently, we developed various deuterated alkyl (dn-alkyl) sulfonium salts based on the H/D exchange reaction of the corresponding hydrogen form using D2O as an inexpensive deuterium source to introduce CD3, CH3CD2, and ArCH2CD2 groups into drug candidates. This concept summarises recent reviews related to H/D exchange reactions and novel reagents that introduce the CD3 group, and our newly developed electrophilic dn-alkyl reagents are discussed.

10) Oxidative Coupling of Hydroquinone Derivatives with Olefins to Dihydrobenzofurans
Yoshinari Sawama, Keiichiro Nakajima, Takaaki Aijima, Miyu Mae, Shinsuke Komagawa, Hiroki Nakata, Hironao Sajiki, and Shuji Akai
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2024,72, 566-569. (Open Access)
DOI: doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c24-00231
selected as Featured Article
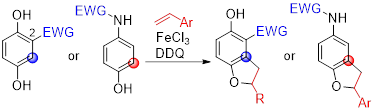
Abstract: Dihydrobenzofuran is an important skeleton for bioactive compounds and natural products. Hydroquinones can be easily modified into substituted hydroquinones, which effectively undergo oxidation to produce the corresponding benzoquinone derivatives. Benzoquinones are reactive electrophiles that are frequently utilized in coupling with olefins to dihydrobenzofurans. Herein, we report the one-pot oxidative coupling of hydroquinones bearing an electron-withdrawing group at the C2 position with olefins to dihydrobenzofurans in the presence of the Lewis acidic FeCl3 and 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-p-benzoquinone (DDQ) oxidant. Furthermore, this method was applied to the oxidative coupling of N-electron-withdrawing group-substituted 4-aminophenol.

9) Light-controllable cell-membrane disturbance for intracellular delivery
Wenting Huo, Koji Miki*, Huiying Mu, Takashi Osawa, Harumi Yamaguma,Yuuya Kasahara, Satoshi Obika, Yoshimasa Kawaguchi, Hisaaki Hirose, Shiroh Futaki, Yusuke Miyazaki, Wataru Shinoda, Shuji Akai and Kouichi Ohe*
Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2024, 12, 4138 – 4147 Open access, front cover
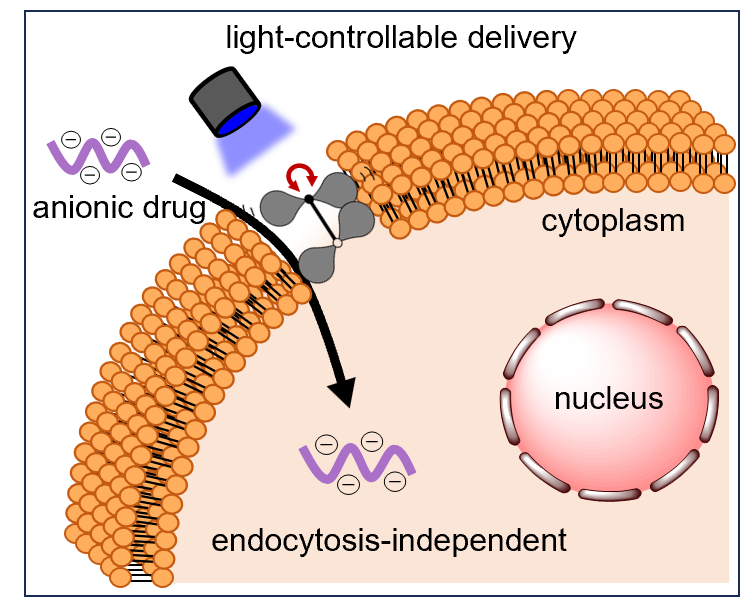

Abstract: Highly polar and charged molecules, such as oligonucleotides, face significant barriers in crossing the cell membrane to access the cytoplasm. To address this problem, we developed a light-triggered twistable tetraphenylethene (TPE) derivative, TPE-C-N, to facilitate the intracellular delivery of charged molecules through an endocytosis-independent pathway. The central double bond of TPE in TPE-C-N is planar in the ground state but becomes twisted in the excited state. Under light irradiation, this planar-to-twisted structural change induces continuous cell membrane disturbances. Such disturbance does not lead to permanent damage to the cell membrane. TPE-C-N significantly enhanced the intracellular delivery of negatively charged molecules under light irradiation when endocytosis was inhibited through low-temperature treatment, confirming the endocytosis-independent nature of this delivery method.
We have successfully demonstrated that the TPE-C-N-mediated light-controllable method can efficiently promote the intracellular delivery of charged molecules, such as peptides and oligonucleotides, with molecular weights ranging from 1000 to 5000 Da.

8) Protein engineering of lipase A from Candida antarctica to improve esterification of tertiary alcohols
Karla Wagner, Anke Hummel, Jianing Yang, Satoshi Horino, Kyohei Kanomata, Shuji Akai* and Harald Gröger*
ChemBioChem, 2024, 25, e202400082
DOI: doi.org/10.1002/cbic.202400082
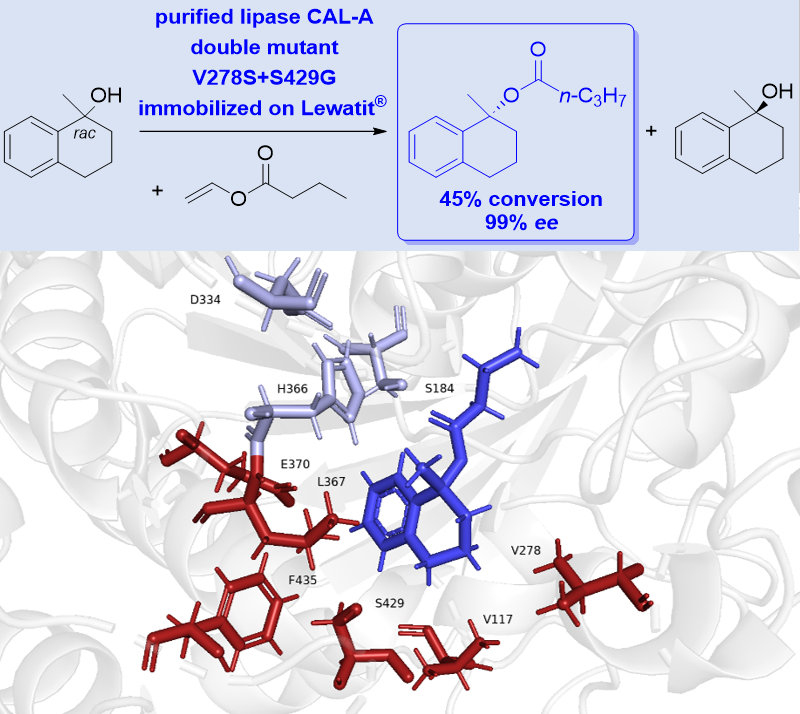
Abstract: Chiral tertiary alcohols are important organic compounds in science as well as in industry. However, their preparation in enantiomerically pure form is still a challenge due to their complex structure and steric hindrances compared with primary and secondary alcohols, so kinetic resolution could be an attractive approach. Lipase A from Candida antarctica (CAL-A) has been shown to catalyze the enantioselective esterification of various tertiary alcohols with excellent enantioselectivity but low activity. Here we report a mutagenesis study by rational design to improve CAL-A activity against tertiary alcohols. Single mutants of CAL-A were selected, expressed, immobilized and screened for esterification of the tertiary alcohol 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene-1-ol. A double mutant V278S+S429G showed a 1.5-fold higher reaction rate than that of the wild type CAL-A, while maintaining excellent enantioselectivity.

7) Strategies to Design Chemocatalytic Racemization of Tertiary Alcohols: State of the Art & Utilization for Dynamic Kinetic Resolution (Open access)
Harald Gröger, Satoshi Horino, Kyohei Kanomata, Shuji Akai
Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202304028
DOI: doi.org/10.1002/chem.202304028
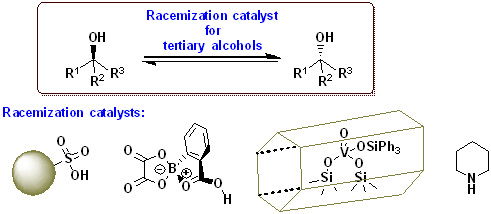
Abstract: In this “Concepts”-article, the difficulties in racemizing tertiary alcohols are described as well as a summary of the different chemocatalytic concepts to overcome these hurdles and to pave a way for efficiently racemizing of tertiary alcohols. When combined with the enantioselective enzymatic esterification of tertiary alcohols, the racemization protocols enable a DKR to convert the racemates into enantiomerically pure esters of tertiary alcohols, which are of high interest in the field of pharmaceutically active products. Very recently, various research groups have succeeded in solving the challenging task of identifying suitable chemocatalysts for an efficient racemization of tertiary alcohols and simultaneously suppressing unwanted dehydration side-reactions. It is noteworthy that such methods are based on different, complementary catalysis concepts. Besides Brønsted acids, oxovanadium catalysts as well as piperidine as a representative of an organocatalyst have been found to be useful for the racemization of each type of alcohols. The latter two types of catalysts also turned out to be compatible with lipase-catalyzed kinetic resolution, thus leading to the first two examples of a proof-of-concept for chemoenzymatic DKR of tertiary alcohols.

6) Kinetic Resolution of Cyclic Tertiary Alcohols with Lipase A from Candida Antarctica
Satoshi Horino, Karla Wagner, Anke Hummel, Kyohei Kanomata, Harald Gröger, Shuji Akai
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 27, e202400242
DOI: doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202400242
大阪大学リポジトリOUKA(オープンアクセス)https://hdl.handle.net/11094/96482
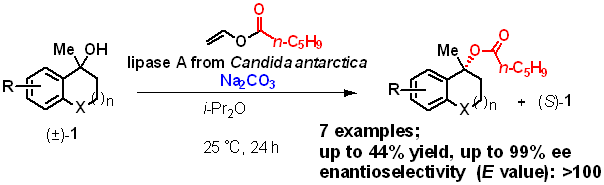

Abstract: Enzyme-catalyzed acylative kinetic resolution (KR) and dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) of racemic primary and secondary alcohols have been widely reported to produce esters with high enantiomeric purity. In contrast, similar KRs of tertiary alcohols have been reported for only a limited range of substrates and require prolonged reaction times of several days. To gain deeper insight into the substrate scope and increase the process efficiency, we examined the reaction conditions using commercially available immobilized lipase A from Candida antarctica and found that the addition of the heterogeneous, inorganic base sodium carbonate significantly increased the reaction rate while maintaining high enantioselectivity. The use of vinyl hexanoate as the acyl donor provided esters that were stable during chromatography purification. The optimized reaction conditions were then successfully applied to a range of cyclic tertiary alcohols containing tetralin, dihydroindene, chromane, and thiochromane skeletons having, in part, a substituent on the aromatic ring. In this study on the structure–reactivity relationship of enzymatic KR-type reactions, we achieved >30% conversion for various tertiary alcohols in 24 h at 25 °C, producing optically active esters with 88–99% ee.

5) 「位置選択的重水素化ならびに多重重水素化の開発と創薬への利用」
澤間善成、赤井周司
未来社会共創を目指す研究シーズ集2024 p.33
研究シーズ集2024の「大阪大学×SDGs」ウェブサイト

4) Versatile Biaryls and Fused Aromatics through Oxidative Coupling of Hydroquinones with (Hetero)Arenes
Takaaki Aijima, Rina Ueda, Takanori Nakane, Fumiaki Makino, Yusuke Ohnishi, Jin Tokunaga, Keiichiro Nakajima, Shinichiro Kamino, Genji Kurisu, Keiichi Namba, Hiroki Nakata, Kaiki Mogi, Hironao Sajiki, Shuji Akai, and Yoshinari Sawama
ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202400647 (Open Access)
XRDa: https://xrda.pdbj.org/entry/162
CCDC: https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/Search?Ccdcid=2294744&DatabaseToSearch=Published
COD: https://www.crystallography.net/cod/3000464.html

Abstract: Hydroquinones bearing an electron-withdrawing group at the C2-position can effectively underwent oxidative coupling with (hetero)arenes (e.g., indoles, electron-rich benzene derivatives) in the presence of 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-p-benzoquinone (DDQ) and FeCl3 to produce the corresponding biaryl products. In the present reactions, the DDQ-mediated oxidation of hydroquinone derivatives produce benzoquinone intermediate, which subsequently underwent FeCl3-catalyzed nucleophilic addition of (hetero)arenes to the a,b-unsaturated carbonyl moiety to give the biaryl product in a one-pot manner. Especially, the indole-based biaryl products were further converted into tetracyclic aromatics through DDQ-mediated oxidation followed by FeCl3-catalyzed intramolecular cyclization. Thiophene derivatives were also applicable to give the tetracyclic aromatics. Moreover, the photophysical properties of the indole- and thiophene-based tetracyclic aromatics in the solution and the solid states were investigated.

3) Nucleophilic Deprotection of p-Methoxybenzyl Ethers Using Heterogeneous Oxovanadium Catalyst
Rei Ikeda, Tomoya Nishio, Kyohei Kanomata , Shuji Akai
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 72, 2, 213-219
DOI:10.1248/cpb.c23-00897
Featured Article
大阪大学リポジトリOUKA(オープンアクセス)https://hdl.handle.net/11094/94660

Abstract: Nucleophilic deprotection of p-methoxybenzyl (PMB) [p-methoxyphenylmethyl (MPM)] ethers was developed using a heterogeneous oxovanadium catalyst V-MPS4 and a thiol nucleophile. The deprotection method had a wide reaction scope, including PMB ethers of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols bearing various functional groups. In addition, the PMB ether of an oxidation-labile natural product was successfully removed by V-MPS4 catalysis, while a common oxidative method of PMB deprotection afforded a complex mixture. The V-MPS4 catalyst was reusable up to six times without a significant loss in the product yield. The advantages of using the heterogeneous catalyst were further demonstrated by conducting the deprotection reaction in a continuous flow process, which resulted in a 2.7-fold higher catalyst turnover number and 60-fold higher turnover frequency compared to those of the corresponding batch reaction.

2) Furanyl Bis(indolyl)methane as a Palladium Ion-Selective Chromogenic Agent
Kazuho Ban, Shiho Nozaki, Takaaki Aijima, Shuki Oyama, Hirofumi Tsujino, Yusuke Kanematsu, Shuji Akai and Yoshinari Sawama
Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 2734–2738. Selected as Outside front cover
DOI:10.1039/D4OB00046C


Abstract: The colorless solution of furan-2-yl bis(indolyl)methanes (BIMs) were newly reveled to work as palladium (Pd2+) ion-selective chromogenic agent to turn orange. 5-(N-methyl-N-phenyl-aminomethyl)-furan-2-yl BIM could be synthesized from 5-chloromethylfurfural as a biorenewable feedstock via one pot and double functionalizations, and a mixture of its solution and Pd2+ ion indicated the highest absorbance at 465 nm in UV-Vis analysis. On the other hand, other metal ions (Cu2+, Cr2+, Cr3+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Ni2+, Zn2+, In2+, Pt2+, or Ce3+) possessed no response.

1) First atroposelective Chan–Lam coupling for the synthesis of C–N linked biaryls
Moeka Ishida, Rina Adachi, Kazuki Kobayashi, Yukiko Yamamoto, Chinatsu Kawahara, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Hiroshi Aoyama, Kyohei Kanomata, Shuji Akai, Patrick Y. S. Lam, Hironao Sajiki and Takashi Ikawa
Chem. Commun., 2024, 60, 678–681
DOI: 10.1039/D3CC05447K
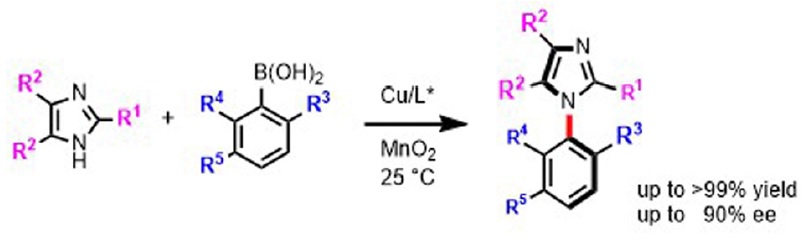

Abstract: The first atroposelective Chan–Lam coupling for the synthesis of C–N axial enantiomers is reported with good yields and ee. MnO2 additive is crucial for the success of the coupling. The longstanding problem of the lack of enantioselective synthesis to make chiral C–N linked atropisomers is solved.