10) 生体関連の有機工業化学 Industrial organic chemistry of bioactive molecules
赤井周司(Shuji Akai), 神戸宣明, 角井神次, 冨田育義, 中 建介, 中山健一, 西山 豊, 益山新樹, 安田 誠
“現代有機工業化学 Modern Organic Industrial Chemistry”, 神戸宣明, 安田 誠編, 化学同人, ISBN: 9784759820256, 発行2020/06/01

9) Continuous-Flow Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Alcohols by Lipase–Oxovanadium Cocatalysis
Koichi Higashio, Satoko Katsuragi, Dhiman Kundu, Niklas Adebar, Carmen Plass, Franziska Kühn, Harald Gröger,* Shuji Akai*
Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2020, 1961-1967.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202000186

Abstract: A continuous-flow dynamic kinetic resolution of racemic secondary alcohols was carried out using a single column reactor packed with a mixture of immobilized lipase and an immobilized oxovanadium species, VMPS4. As a result, optically pure esters were produced in 88–92% yields. Problems encountered in this study were overcome by using fillers that efficiently maintained the initial distribution of the catalysts in the reactor and by using a packing method in which the mixing ratio of the two catalysts was varied in a stepwise fashion. The flow process led to an increased turnover number of each catalyst compared to those of batch reactions.
8) One-Pot Formal Dehydrogenative Ketone Synthesis from Aldehydes and Non-activated Hydrocarbons,
Kenzo Yahata,* Shin Yoshioka, Shuhei Hori, Shu Sakurai, Yuki Kaneko, Kai Hasegawa, Shuji Akai
Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2020, 68, 336–338.
doi: 10.1248/cpb.c20-00075

Abstract: Ketones are a fundamental functionality found throughout a range of natural and synthetic compounds, making their synthesis essential throughout the chemical disciplines. Herein, we describe a one-pot synthesis of ketones via decatungstate-mediated dehydrogenative coupling between aldehydes and non-activated hydrocarbons. A variety of substituted benzaldehydes and cycloalkanes could be used in the optimized reaction to produce the desired ketones in moderate yields. The decatungstate photocatalyst functions in two reactions in this synthesis, catalyzing both the coupling and oxidation steps of the process. Notably, the reaction displays both high atom economy and sustainability, as it uses light and oxygen as key energy sources.
7) Cobalt-catalyzed Hydroamination of Alkenes with 5-Substituted Tetrazoles: Facile access to 2,5-Disubstituted Tetrazoles and Asymmetric Intermolecular Hydroaminations
Kenzo Yahata,* Yuki Kaneko, and Shuji Akai*
Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2020, 68, 332–335.
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c20-00068

Abstract: Herein, we describe a novel synthetic method for 2,5-disubstituted tetrazoles from 5-substituted tetrazoles using cobalt-catalyzed intermolecular hydroamination reaction of nonactivated olefins. Owing to its mild conditions, the method enabled the use of substrates having acid-labile functional groups, such as silyloxy and methoxymethyloxy groups. By using optically active cobalt complexes, asymmetric intermolecular hydroamination of nonactivated olefins, a longstanding challenge in synthetic organic chemistry, was developed to produce optically active disubstituted tetrazoles.
6) Dynamic kinetic resolution of a tertiary alcohol
Franziska Kühn, Satoko Katsuragi, Yasuhiro Oki, Cedric Scholz, Shuji Akai,* Harald Gröger*
Chem. Comuun., 2020, 56, 2885-2888.
DOI: 10.1039/C9CC09103C

Abstract: In spite of the tremendous success of dynamic kinetic resolutions for a broad range of compound classes, tertiary alcohols and their corresponding esters have still remained as one of the most challenging substrates for this type of process. This is due to the size and steric hindrance of tertiary alcohol as well as to the difficulty in finding reaction conditions for the racemization of such compounds being at the same time compatible with the resolution reaction, which preferably is carried out with an enzyme. In this study, the first example of a dynamic kinetic resolution of a racemic tertiary alcohol is presented. The desired synthesis of the resulting enantiomerically pure ester was achieved by combining a lipase-catalyzed kinetic resolution with an in situ racemization utilizing a bio-compatible oxovanadium-catalyst. First, the two individual reactions were examined, improved and adjusted to be compatible with each other. Subsequently, addition of both catalysts in tailor-made portions led to the desired combined process and delivered the product with >99% ee and a conversion exceeding 50%, thus proving such a desired dynamic kinetic resolution of a tertiary alcohol.
5) Coupling Reaction between Aldehydes and Non-Activated Hydrocarbons via the Reductive Radical-Polar Crossover Pathway
Kenzo Yahata,* Shu Sakurai, Shuhei Hori, Shin Yoshioka, Yuki Kaneko, Kai Hasegawa, Shuji Akai
Org. Lett., 2020, 22, 1199−1203.
https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00096

Abstract: Herein, we describe the generation of an organochromium-type carbanion species from a non-activated C−H bond and its nucleophilic addition to aldehydes. The catalytic carbanion generation occurred through formal deprotonation of a non-activated C−H bond under mild conditions and did not need the prefunctionalization or anion stabilizing group. Carbon radical intermediates generated by decatungstate photocatalyst-mediated hydrogen abstraction were captured by a chromium salt with the reductive radical-polar crossover reaction to produce organochromium carbanions.
4) One-Pot Generation of Functionalized Benzynes from Readily Available 2-Hydroxyphenylboronic Acids
Takashi Ikawa,* JingKai Sun, Akira Takagi, Shuji Akai*
J. Org. Chem., 2020, 85, 3383-3392.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.9b03169

Abstract: We developed a one-pot method for the generation of benzynes from a range of readily available 2-hydroxyphenylboronic acids. This method features the in-situ activation of both boronic acid and hydroxyl groups of the substrate to enhance benzyne generation at 60 °C. Such mild conditions facilitate the generation of functionalized benzynes that immediately react with diverse arynophiles to produce multi-substituted fused benzenes.
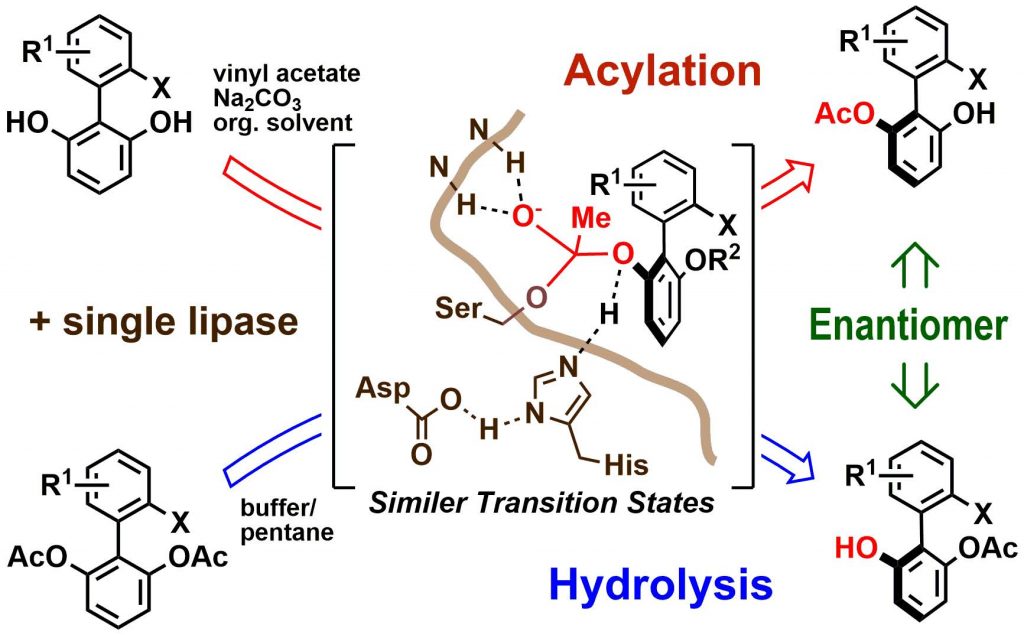
3) Enantiodivergent synthesis of axially chiral biphenyls from σ-symmetric 1,1ʹ-biphenyl-2,6-diol derivatives by single lipase-catalyzed acylative and hydrolytic desymmetrization
Kengo Kasama, Hiroshi Aoyama, Shuji Akai *
Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2020, 654–661.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201901583
Cited as a cover picture.
Abstract: The enzymatic acylative desymmetrization of σ-symmetric 2’-halo-1,1ʹ-biphenyl-2,6-diolswas achieved for the first time using commercially available Burkholderia cepacia lipase immobilized on diatomaceous earth to give (S)-mono esters. The hydrolytic desymmetrization of the corresponding diacetateswas also achieved using the same lipase to give (R)-mono esters. Our results therefore demonstrate that a single lipase can conduct the enantiodivergent synthesis of axially chiral biphenyl compounds in high chemical and optical yields.
2) Cobalt-Catalyzed Intermolecular Markovnikov Hydroamination of Nonactivated Olefins: N2‑Selective Alkylation of Benzotriazole
Kenzo Yahata,* Yuki Kaneko, and Shuji Akai*
Org. Lett., 2020, 22, 598-603.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b04375

Abstract: Cobalt-catalyzed Markovnikov-selective hydroamination of nonactivated olefins was developed. Hydrogen atom transfer from a catalytically generated cobalt(III)−hydride complex to the olefins proceeded regioselectively, and the nucleophilic addition of benzotriazoles occurred selectively at their N2-positions. The synthetic utility of the obtained N2-alkylated benzotriazoles as stable amine protecting groups under various reaction conditions was demonstrated, and the products were also transformed into primary amines by zinc-mediated reduction.
1) One-Pot Generation of Benzynes from Phenols: Formation of Primary Anilines by the Deoxyamination of Phenols
Takashi Ikawa,* Shigeaki Masuda, and Shuji Akai*
Chem. Eur. J., 2020, 26, 4320-4332.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201904987

Abstract: Benzynes were selectively generated in-situ from phenols and trapped regioselectively by potassium hexamethyldisilazide to form primary anilines following acidic workup. The direct conversion of a phenolic hydroxyl group to a free amino group is a useful method for the preparation of primary aryl amines that are hard to synthesize using coupling reactions involving phenol derivatives with ammonia. While reactions of ortho– and meta-substituted phenols produced meta-substituted anilines exclusively, those of para-substituted phenols provided ortho-silylanilines.