13) Synthetic Studies Toward Rubioncolin B
Takaaki Aijima, Shuji Akai, Yoshinari Sawama
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2026, 29, e202501103.
DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.202501103
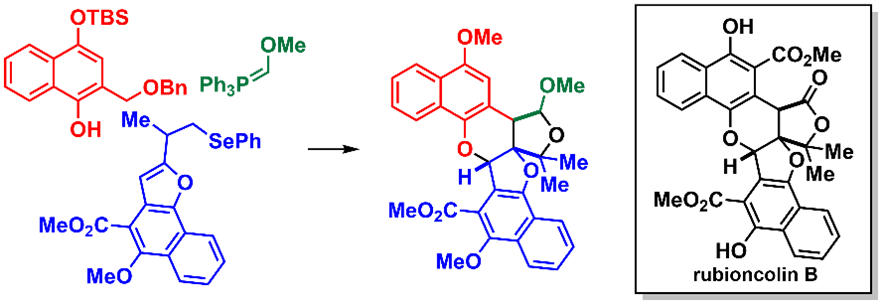
Abstract: Herein, we report our synthetic studies toward rubioncolin B (1), a heptacyclic naphthohydroquinone dimer with antitumor activity. Our strategy is based on the intermolecular [4 + 2]-cycloaddition reaction between an ortho-naphthoquinone methide (o-NQM), which is generated in situ from a 1-naphthol derivative under catalytic Lewis acid conditions, and a naphthofuran derivative, thereby enabling the construction of a hexacyclic compound. We then explored three synthetic approaches for appending the remaining ring structure to the hexacyclic compound. Among them, the sequence involving the introduction of a Wittig reagent and subsequent cyclization proved effective, furnishing a cyclic acetal with the same ring structure as 1. This strategy not only demonstrates that accessing the highly congested architecture of 1 is feasible but also provides a versatile platform for the synthesis of structurally diverse analogs, thereby facilitating subsequent biological investigations, including structure–activity relationship studies.

12) Chemoenzymatic Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of a Tertiary Alcohol Based on Compartmentalization of Oxovanadium and Lipase Catalysts by Means of a Polydimethylsiloxane Thimble
Karla Wagner, Satoshi Horino, Anke Hummel, Kyohei Kanomata, Shuji Akai, Harald Gröger
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2025, 73, 511-514.
DOI: 10.1248/cpb.c25-00065
Abstoract: Addressing the challenging field of chemoenzymatic dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) of tertiary alcohols, for which so far only one example exists in the literature, we combined biocatalytic esterification and oxovanadium-catalyzed racemization, operating both steps in two different compartments of one reactor. The compartmentalization of the two heterogeneous catalysts, namely, immobilized lipase A from Candida antarctica (CAL-A) or its mutant and oxovanadium species on mesoporous silica, was achieved using a polydimethylsiloxane thimble, avoiding contact of the oxovanadium with water, thus maintaining the catalyst’s activity and thereby successfully improving the efficiency of the DKR. Utilizing the immobilized double mutant CAL-A V278S + S429G, the ester was obtained in 62% yield with excellent enantiomeric excess of >99% ee.

11) Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reaction of 4-Aminophenols with 2-Naphthols Catalyzed by a Mesoporous Silica-Supported Oxovanadium Catalyst
Yutaro Ito, Kengo Kasama, Jihoon Moon, Yui Kanzaki, Tomoya Nishio, Koichiro Masuda, Kwihwan Kobayashi, Atsushi Kimishima, Hiroshi Aoyama, Kyohei Kanomata, Shuji Akai
Asian J. Org. Chem. 2025, 14, e0057.(オープンアクセス)
DOI:10.1002/ajoc.202500537
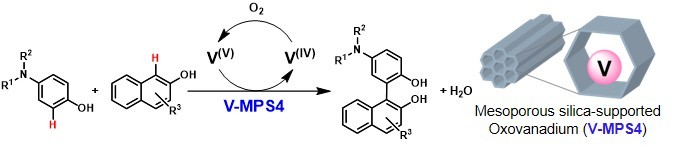
Abstoract: Cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) reactions offer an atom-economical approach for synthesizing biaryl compounds by directly forming C─C bonds from the C─H bonds of two aromatic molecules. In this study, the CDC reaction between 4-aminophenols and 2-naphthols was successfully catalyzed using a mesoporous silica-supported oxovanadium catalyst. This reaction involved the catalytic, chemo- and regio-selective oxidation of 4-aminophenols, with molecular oxygen as the terminal oxidant, eliminating the need for stoichiometric chemical oxidants, thereby making the reaction more environmentally friendly.

10) 有機分子に重水素を直接導入する手法(重水素化)の開発
澤間善成
理論化学会会誌「フロンティア」特集:重水素の化学

9) Pickeringエマルションを反応場とする多段階連続触媒反応の新設計戦略
鹿又喬平, 薬学雑誌, 2025, 145, 833-842. (オープンアクセス)
DOI: 10.1248/yakushi.25-00120
Abstoract: Enantiomers of a chiral compound often exhibit distinct physiological activities, making enantioselective synthesis of chiral molecules a critical challenge in drug discovery. This study explored a novel strategy for converting racemic compounds into a single enantiomer using enzymes, with a focus on developing a methodology to access both enantiomers of chiral esters using a single lipase and enantioconvergent reactions of tertiary alcohols. The desired transformations were achieved by designing multi-catalytic systems that enabled lipases to combine with otherwise incompatible catalysts and reactants using Pickering emulsions as compartmentalized reaction media.

8) Lipase-Catalyzed Kinetic Resolution Followed by an Intramolecular Diels–Alder Reaction: Enantio- and Diastereoselective Synthesis of an A-Ring Moiety of Furanosteroids
Chiharu Yuki, Shuhei Hori, Satoshi Horino, Hiroshi Aoyama, Kyohei Kanomata, Shuji Akai
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2025, 73, 663–669.
Abstoract: Furanosteroids are known to exhibit inhibitory activity against phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase and are expected to serve as a basis for the development of therapeutic drugs for various diseases. In this study, a novel protocol is presented for preparation of the furanosteroid A-ring moiety. More specifically, the lipase-catalyzed kinetic resolution of racemic 1-(3-bromofuran-2-yl)-2-chloroethanol with β-substituted (Z)-acrylates and the subsequent intramolecular Diels–Alder reaction of the generated enantiomerically enriched esters were performed to obtain multi-functionalized fused cyclohexenes in excellent enantiomeric ratios (99 : 1 or 98% enantiomeric excess (ee)) and diastereomeric ratios (≥98 : 2). The obtained products possess the appropriate stereochemical structures and absolute configuration for use in the asymmetric synthesis of the A-ring moieties of naturally occurring furanosteroids, including viridin and viridol.

7) Dynamic kinetic resolution of tert-alcohols via combination of a lipase/Brønsted acid in a biphasic reaction medium
Takusho Kin, Satoshi Horino, Jihoon Moon, Momoka Tsuda, Harald Gröger, Shuji Akai, Kyohei Kanomata
Green Chem. 2025, 27, 9672-9678.
大阪大学リポジトリOUKA(オープンアクセス)https://hdl.handle.net/11094/102428(2026-7-10公開)
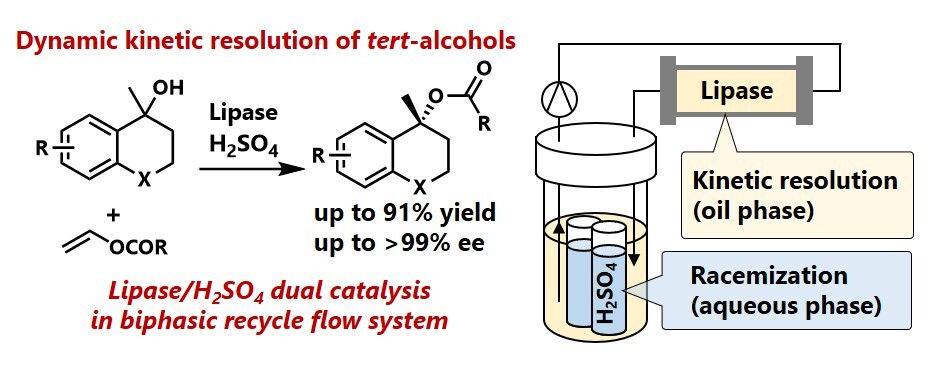

Abstoract: Chemoenzymatic dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) provides a promising green approach for synthesizing optically active alcohols and their derivatives, which serve as widely used key intermediates in the fine chemical industry. While lipase-catalysed DKR of secondary alcohols has been extensively studied, the DKR of tertiary alcohols remains a significant challenge, even in advanced organic synthesis. This is mainly because tert-alcohols are poorly reactive to esterification owing to steric hindrance and are prone to dehydrative side reactions. In this study, the combined use of a lipase and the strong Brønsted acid H2SO4 enabled the efficient DKR of racemic tert-alcohols to produce the corresponding esters with high enantiomeric excess (95–99% ee) in 56–91% isolated yields. In this DKR system, lipase-catalysed kinetic resolution in the oil phase and H2SO4-catalysed racemization of the unreacted enantiomer of the alcohol in the aqueous phase proceeded concurrently in one reactor. This simultaneous use of the inherently incompatible combination of a lipase and a strong Brønsted acid was realized by integrating phase separation via a hydrophobic polydimethylsiloxane membrane and a recycling flow reaction system. In addition, side reactions were completely suppressed by conducting the racemization reaction in the aqueous phase, enabling the application of this DKR methodology to a range of tert-alcohols, thus demonstrating, for the first time, a generally applicable DKR system for tert-alcohols.

6) Lipase-palladium co-catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution of racemic allylic esters
Masato Oono, Akane Yamada, Masanari Kimura, Kyohei Kanomata, Shuji Akai
Chem. Eur. J. 2025, 31, e202404406.
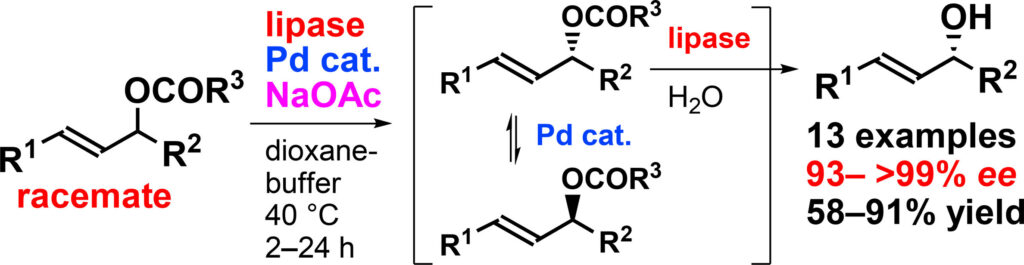
Abstract: Dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) by combining lipase-catalyzed esterification of racemic sec-alcohols and in situ racemization has been widely studied; however, reports on DKR involving lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of racemic esters are scarce. This problem is probably due to the lack of more effective and general racemization methods. Herein, we report the enhanced hydrolytic DKR of racemic allylic esters. The discovery of the monodentate ligand P[C6H3-2,6-(OMe)2]3, which in situ generates Pd complex(es) highly reactive to racemization and the NaOAc-mediated acceleration of racemization, are notable breakthroughs. Consequently, the DKR of racemic allylic esters can be completed in a few hours at 40 °C in most cases, yielding optically active allylic alcohols (93 % ee to >99 % ee) in 58–91 % isolated yields with minimal side reactions.

5) Photocatalytic and Chemoselective H/D Exchange at a-thio C(sp3)-H Bonds
R. Ogasahara,‡ M. Mae,‡ Y. Itabashi, K. Ohkubo, K. Matsuura, H. Shimizu, K. Ban, M. Togami, T. Udagawa, H. Fujioka, M. Kamiya, S. Akai, Y. Sawama*
‡ equally contributed
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, just accepted.
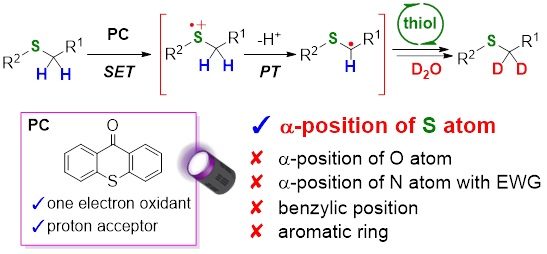
Abstract: Deuterated compounds used in drug discovery and live-cell imaging have recently gained the attention of various scientific fields. Although hydrogen-deuterium (H/D) exchange reactions are straightforward deuteration methods, achieving perfect chemoselectivity is challenging. We report the highly chemoselective deuteration of a-thio C(sp3)-H bonds using a thioxanthone or anthraquinone organic photocatalyst bearing an aromatic ketone skeleton and D2O as an inexpensive deuterium source under 390 nm irradiation. Notably, deuterium incorporation at the a-positions of O/N atoms, benzylic positions, and aromatic rings was not observed. The present chemoselectivity was accomplished via a single electron transfer mechanism between the photocatalyst and S-containing substrates, as proven by laser-induced time-resolved transient absorption spectroscopic measurements. Furthermore, the proposed deuteration method could be applied to various S-containing substrates including pharmaceuticals and biologically active compounds with high regioselectivities. The available deuterated compounds as novel deuterated alkylation reagents for future drug discovery and as materials for Raman imaging were also demonstrated.

4) Photocatalytic Multiple Deuteration of Polyethylene Glycol Derivatives Using Deuterium Oxide
R. Ogasahara, M. Mae, K. Matsuura, S. Yoshimura, T. Ishimoto, T. Udagawa, K. Harada, H. Fujioka, M. Kamiya, R. Asada, H. Uchiyama, Y. Tozuka, S. Akai, Y. Sawama*
Chem. Eur. J. 2025, e202404204
DOI: doi.org/10.1002/chem.202404204
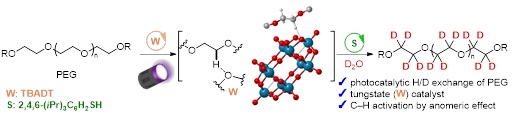
Abstract: Deuterated molecules are of growing interest because of the specific characteristics of deuterium, such as stronger C-D bonds being stronger than C-H bonds. Polyethylene glycols (PEGs) are widely utilized in scientific fields (e.g., drug discovery and material sciences) as linkers and for the improvement of various properties (solubility in water, stability, etc.) of mother compounds. Therefore, deuterated PEGs can be used as novel tools for drug discovery. Although the H/D exchange reaction (deuteration) is a powerful and straightforward method to produce deuterated compounds, the deuteration of PEGs bearing many unactivated C(sp3)-H bonds has not been developed. Herein, we report the photocatalytic deuteration of multiple sites of PEGs using tetra-n-butylammonium decatungstate (TBADT) and D2O as an inexpensive deuterium source. This deuteration can be adapted to PEG derivatives bearing various substituents ((hetero)aryl, benzoyl, alkyl, etc.). The deuteration efficiencies of the a-oxy C(sp3)-H bonds at the terminal positions of the PEGs were strongly influenced by the substituents. These reactivities were elucidated by density functional theory calculations of the reaction barriers towards the formation of radical intermediates, induced by the excited state of TBADT and the PEG substrate. In addition, the applicability of deuterated PEGs to internal standard experiments and Raman spectroscopy was demonstrated.

3) Total synthesis of aloin via regioselective Diels–Alder reactions connecting two 3-silylbenzynes and 2-stannylfuran
S. Moriyama, Y. Emi, T. Nosaki, Y. Morikawa, T. Shigeta, A. Takagi, M. Egi, T. Ikawa, Y. Sawama, S. Akai,*
Synlett 2025, 36, A–E
DOI: 10.1055/a-2542-3481
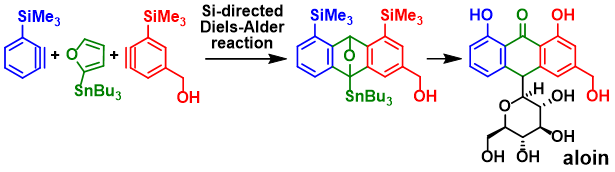
Abstract: The first synthesis of aloin, a natural anthrone C-glycoside, was achieved via two sequential Diels–Alder (DA) reactions connecting 3-silyl-benzynes and 2-stannylfuran. The silyl and stannyl substituents contributed to the regioselectivity of the two DA reactions and the 9,10-ether cleavage of the DA adduct. The subsequent conversion of silyl groups to hydroxyl groups and C10-glycosylation completed the synthesis of aloin.

2) (S)-Convergent Deracemization of Racemic Esters with (R)-Selective Lipase: Pickering Emulsion Strategy for Enantiodivergent Synthesis Using a Native Enzyme
Tomoya Nishio, Shuji Akai, Kyohei Kanomata
ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 6565–6571.
大阪大学リポジトリOUKA(オープンアクセス)https://hdl.handle.net/11094/100944(2026-4-7公開)
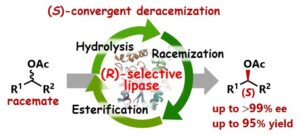
Abstract: Catalytic synthesis of both enantiomers of a chiral molecule typically requires both enantiomers of chiral catalysts. However, a number of chiral catalysts for asymmetric transformations, including enzymes, are naturally available in only one enantiomeric form. In this study, we present an enantiodivergent strategy for enzymatic transformations using a single native enzyme. Specifically, we developed an (S)-convergent deracemization process for racemic esters using a native (R)-selective lipase. The transformation was achieved by integrating three reactions into a single system: (1) lipase-catalyzed (R)-selective hydrolysis of a racemic ester, (2) H2SO4-catalyzed racemization of the resulting (R)-alcohol, and (3) esterification of the racemized alcohol. The use of a Pickering emulsion as the reaction medium facilitated the combination of these inherently incompatible processes by compartmentalizing these reactions. Complementary to the conventional (R)-selective transformation, this approach enables the enantiodivergent synthesis of a wide range of sec-alcohols and their corresponding esters using the same native lipase.

1) Racemization of chiral sulfoxide using an immobilized oxovanadium catalyst
Tomoya Nishio, Hajime Shigemitsu, Toshiyuki Kida, Shuji Akai, Kyohei Kanomata
Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2025, 98, uoae144.
DOI: 10.1093/bulcsj/uoae144
大阪大学リポジトリOUKA(オープンアクセス)https://hdl.handle.net/11094/99973(2025-12-28公開)
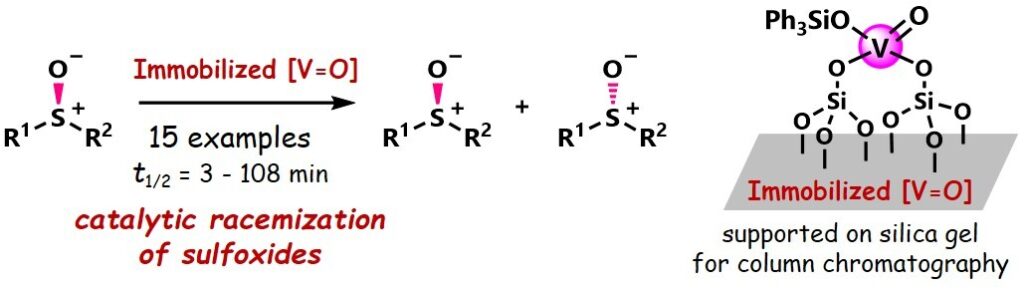
Abstract: Racemization of optically active compounds is an essential process in asymmetric transformations such as dynamic kinetic resolution and deracemization. In this study, the racemization of chiral sulfoxides under mild thermal conditions was realized using a novel silica-gel-supported oxovanadium catalyst. Specifically, we screened reaction conditions, analyzed the substrate scope, and conducted mechanistic studies of the silica-gel-supported oxovanadium-catalyzed racemization of sulfoxides. The racemization reaction has a wide substrate scope, including alkyl aryl sulfoxides and diaryl sulfoxides. The catalyst could be reused by exploiting its heterogeneous nature. Mechanistic studies suggested that racemization proceeds via the formation of a radical cation intermediate mediated by the oxovanadium(V)/(IV) redox cycle.