1) (S)-Convergent Deracemization of Racemic Esters with (R)-Selective Lipase: Pickering Emulsion Strategy for Enantiodivergent Synthesis Using a Native Enzyme
Tomoya Nishio, Shuji Akai, Kyohei Kanomata
ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 6565–6571.
大阪大学リポジトリOUKA(オープンアクセス)https://ir.library.osaka-u.ac.jp/repo/ouka/all/100944/(2025-4-7公開)
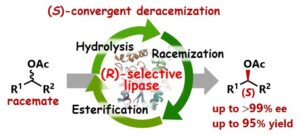
Abstract: Catalytic synthesis of both enantiomers of a chiral molecule typically requires both enantiomers of chiral catalysts. However, a number of chiral catalysts for asymmetric transformations, including enzymes, are naturally available in only one enantiomeric form. In this study, we present an enantiodivergent strategy for enzymatic transformations using a single native enzyme. Specifically, we developed an (S)-convergent deracemization process for racemic esters using a native (R)-selective lipase. The transformation was achieved by integrating three reactions into a single system: (1) lipase-catalyzed (R)-selective hydrolysis of a racemic ester, (2) H2SO4-catalyzed racemization of the resulting (R)-alcohol, and (3) esterification of the racemized alcohol. The use of a Pickering emulsion as the reaction medium facilitated the combination of these inherently incompatible processes by compartmentalizing these reactions. Complementary to the conventional (R)-selective transformation, this approach enables the enantiodivergent synthesis of a wide range of sec-alcohols and their corresponding esters using the same native lipase.